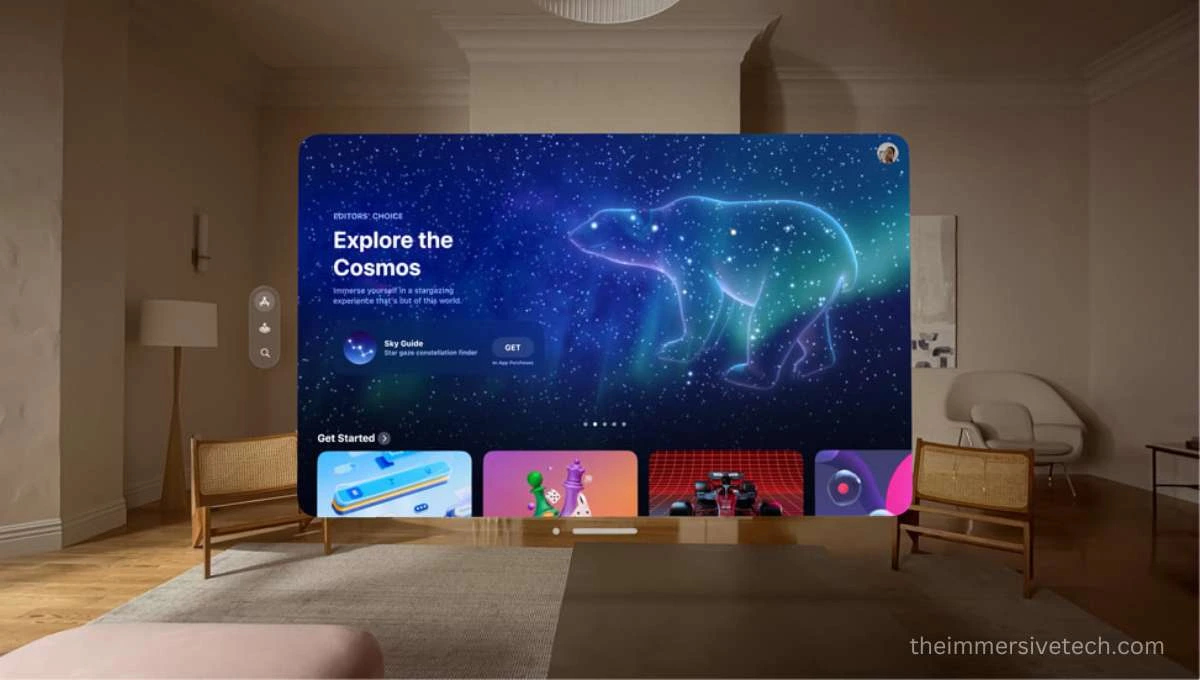
When Apple introduced its first virtual product, The Vision Pro, it marketed the headset clearly as a spatial computer. But like any other VR or MR headset, Apple’s Vision Pro works the same. Then what is so special about spatial computing?
In this article, we will explore what it is and how it’s so different than other technologies.
What is Spatial Computing?
The term ‘spatial computing’ is a broad concept that combines the physical world with the virtual elements. Thus, allowing virtual objects to co-exist and interact with the physical world as if they were actually there. In fact, the technology allows users to interact with the digital objects.
In simple words, spatial computing is a system for computers to interact and understand the physical world. Using this, users can interact with the virtual elements easily.
How Does Spatial Computing Work?
Spatial computing blends the virtual and physical worlds seamlessly. It does so in such a way that you can experience it through headsets like the Apple Vision Pro, Microsoft HoloLens, Meta Quest Pro, and Magic Leap.
These devices can embed virtual objects that appear three-dimensional into the real world. To do so, they combine several technologies to mix the physical and digital worlds. For instance, computer vision processes data from sensors and captures visual information about the environment. This includes the position, orientation, and movement of objects.
Sensor fusion combines the data from different sensors, such as cameras and LiDARs, to create an accurately comprehensive view of the environment. To precisely place and manipulate this digital content, spatial mapping is used to create a 3D model of the space.
How is Spatial Computing So Realistic?
Spatial computing can understand the depth of the environment. It allows the virtual objects to be placed and manipulated in a way that corresponds to the real world, making the user interactions so realistic and natural. For example, a virtual object can be placed on a couch, moved around, or held in a way that feels real.
Devices that use spatial computing have many features that let you interact with the digital world. For instance, eye-tracking technology monitors your view while controllers and motion sensors let you move around the objects just with the pinch of your finger.
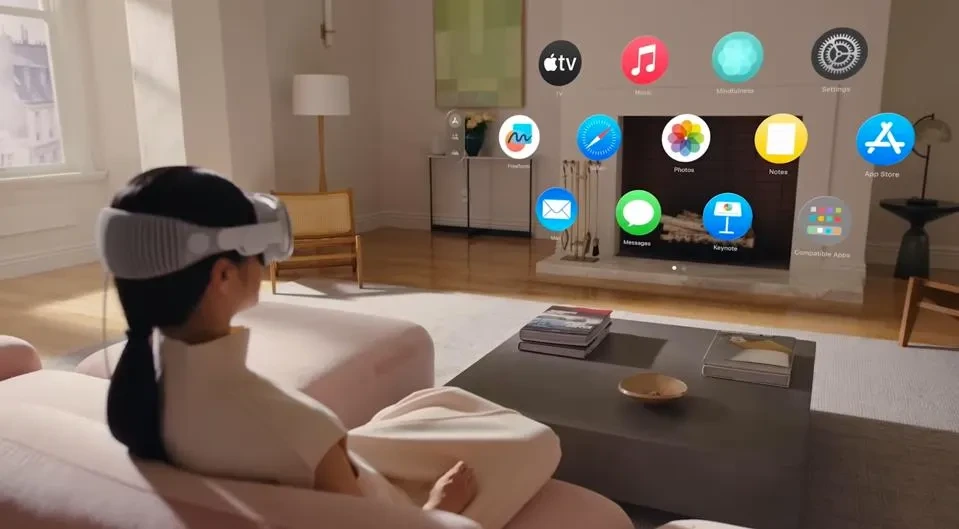

Some devices also have speech recognition features that support voice commands, such as the Vision Pro, HoloLens, and Magic Leap.
Examples of Spatial Computing
There are many examples of spatial computing in the AR and VR world. For instance, Apple describes its Vision Pro headset as a spatial computer. Interesting, right?
However, there are many other examples as well. AR glasses such as Meta’s Ray-Ban smart glasses and Xreal’s Air 2 Ultra represent this technology pretty well. Another VR headset includes the Meta Quest 3 with its 365 virtual capabilities.
Difference Between Spatial Computing, VR, AR, and MR
Any technology that blends together physical and virtual worlds in some way is a part of spatial computing. In simple words, it’s more about the core concept of interacting with digital elements within the physical space.
Hence, all technologies such as augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and mixed reality (MR) are a part of spatial computing. But, what’s the difference between AR, VR, and MR?
Virtual Reality (VR)
Virtual reality creates a completely immersive digital environment that shuts down the physical world. This technology is mainly accessible through VR headsets such as the Quest 2.
Since you cannot see anything around you, the headsets include sensors and cameras which protect you from getting injured. Virtual reality is incredibly popular among gamers with advanced headsets such as PS VR2.
Augmented Reality (AR)
Unlike virtual reality, augmented reality overlays digital elements onto the real world. This doesn’t block the physical world from your sight, but adds virtual objects to it.
You can use AR glasses such as Meta’s recent prototype, “Orion” or smartphone to experience augmented reality. For instance, IKEA’s app allows customers to view how a furniture piece would look like in their home — all through their phone.
Mixed Reality (MR)
Mixed reality is a seamless blend of both AR and VR technologies. It allows users to interact with and manipulate digital objects within the real world.
In addition, digital objects can seamlessly interact with real world objects. For example, you can pick up a virtual book and place it on a real table. Due to such advanced levels of manipulation, MR devices require sophisticated sensors and tracking systems.
All these technologies can be described with one term — Extended Reality or XR. As they blend virtual and real worlds in different ways, they become a part of it.
How is Spatial Computing Used?
Spatial computing is already revolutionizing various industries with extraordinary digital experiences. Some of the most popular ones include gaming and healthcare. Let’s see how this technology is used across these industries:
Gaming and Entertainment
Immersive gaming and movie experiences are possible through spatial computing, which lets you interact with virtual objects and characters in an intuitive way. For instance, you can use your hand gestures or your gaze to control avatars and objects in a game.
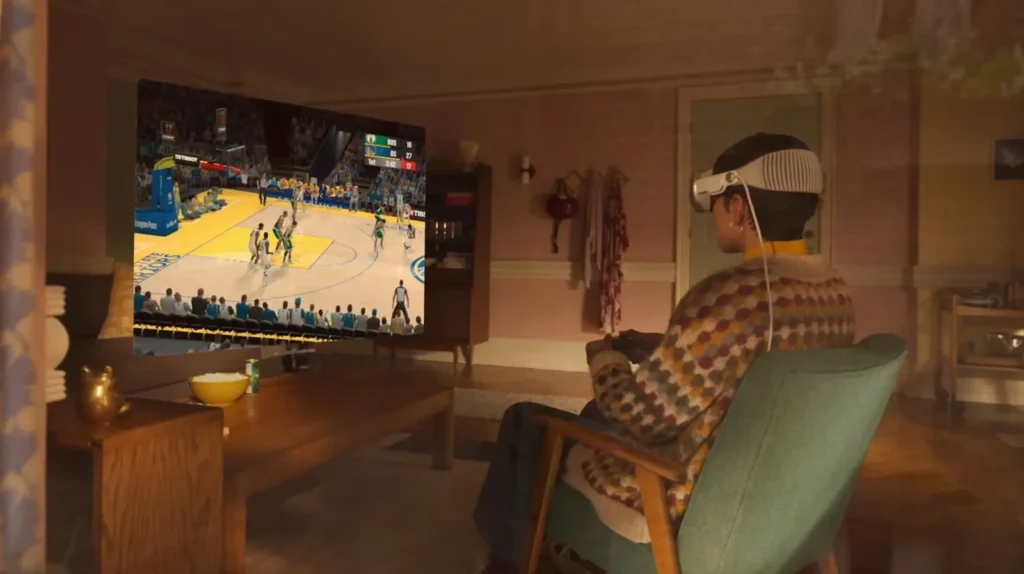

This allows you to experience real-world happenings in a different way. One such example is the Apple Vision Pro using which you can watch an NBA game as if you’re in a court-side seat. It can also record the virtual experience in 3D.
Education and Training
The technology can help create engaging, fun, and interactive learning experiences. Thus, enhancing the learners’ knowledge retention and skills acquisition. Such an experience is particularly helpful for medical students to practice surgical procedures in a virtual environment.
Otherwise, immersive experiences are also helpful in science and engineering. As they allow the students to build and test prototypes virtually, this reduces any waste while conducting experiments.
Architecture and Design
Architects can use spatial computing-based devices to create, visualize, and modify designs in real time without having to create physical prototypes. This helps save time and cost while allowing for a faster design process.
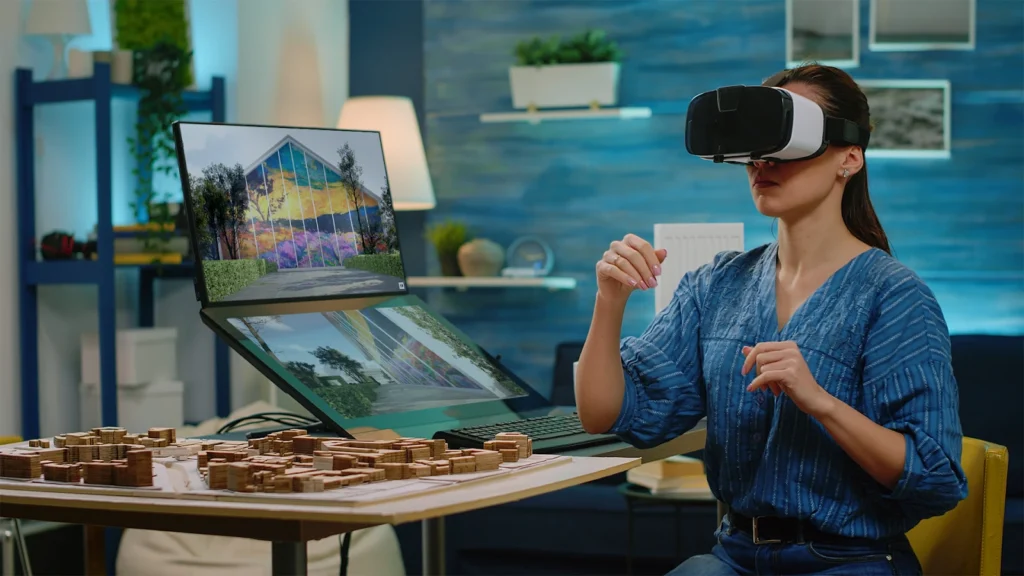

Similarly, designers can use the technology to create virtual prototypes. The real-like appearance also allows them to test their functionality and ergonomics without any hassle in different physical settings.
Healthcare
In healthcare, spatial computing has a wide range of uses — from diagnosis to monitoring patients. For example, doctors could overlay different test results and scans virtually to make more informed decisions.
The technology could also help patients with physical or cognitive impairments with virtual rehabilitation. These exercises are tailored to their needs, helping them recover better.
Apart from these four major sectors, the immersive technology is also used in retail, manufacturing, and transportation.
You may also read: – Practical Applications & Use of VR
The Future of Spatial Computing
While spatial computing has so many advantages, it still falls behind because of its expensive hardware costs. The best devices such as the Vision Pro cost thousands of dollars, making them inaccessible to all. Thus, these devices still haven’t hit their peak success yet.
In addition, factors such as the device’s weight, low resolution, and motion sickness cause concerns among potential users. Low-to-moderate battery life is another limitation. For now, companies such as Meta are making progress with these factors.