Virtual reality has become increasingly popular in the past decade. With the release of Meta’s Quest 3 and Apple’ Vision Pro, it has gained more traction than ever. There are videos circulating the Internet of people working on their way home while wearing VR headsets.
But how does this incredible technology work?
How VR works?
We’ll find that out in this article.
What is Virtual Reality?
Virtual reality is a computer-generated, virtual environment that users can experience by wearing virtual reality headsets or glasses. In a virtual world, users can interact with the virtual elements and modify them in real time. Additionally, VR is not limited to a single space.
There are 3 types of VR: non-immersive, semi-immersive, and fully-immersive. VR headsets provide the fully-immersive experience to the users which fully immerse the users in a 3D virtual environment. Hence, making the users feel as if the virtual environment is real.
To explore more into the basics of virtual reality, check our dedicated blog on “introduction to virtual reality.”
Components of Virtual Reality
1. VR Headset
Virtual reality headsets are wearables that help users immerse into the virtual world. To make that happen, a VR headset replaces the user’s natural field of view with a computer-generated field of view, creating a virtual world.
The components of a VR headset include screens, cameras, motion sensors, and infrared LEDs. All of them enable the headset to gather information and provide it for the human eye. VR headsets can be of many types: wired, wireless, PC-based, or console-based.
2. Lenses and Screens
The screens and lenses ensure that the virtual experience is as real as possible. It happens when two nearly identical images are distorted and overlapped. Hence, creating a 3D and real-like virtual image.
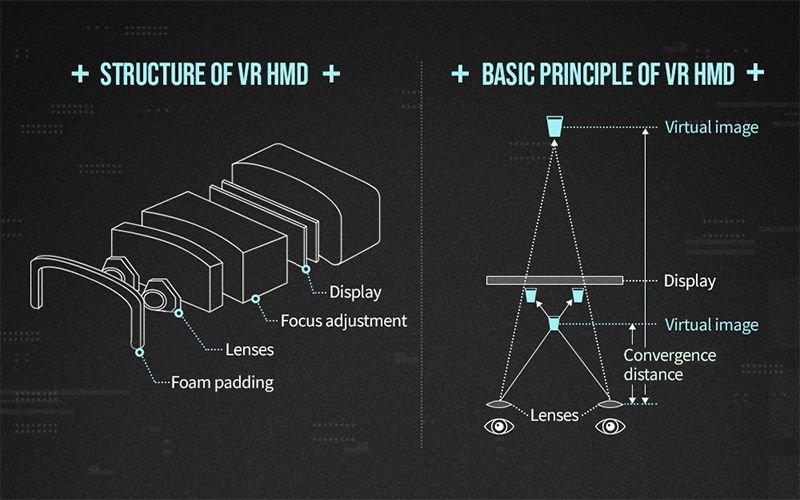
Source: https://www.synopsys.com/
3. Latency and Field of View (FOV)
Latency and FOV are two features that provide virtual information to the real world. Both of them affect the perception of distance and spatial depth in the virtual and real worlds.
Generally, a human eye can see their environment in a 200∘ to 220∘ arc. The eyesight from our left and right eyes overlap at a 114∘ angle, creating a 3D effect. VR headsets use a similar thing to create the instant, virtual 3D effect. They reduce the latency and provide a 114∘ 3D space. However, no headset provides zero latency.
4. Frame rate
Humans can see up to 1,000 images per second, which means 1,000 frames per second (FPS). However, our brain never receives such detail via the optic nerve. Additionally, the information gets lost if the frame rate is too fast. So, most VR headsets aim for the ‘sweet spot’ of 90 FPS.
5. Position tracking
Position tracking is even more crucial than other aspects such as visuals and sounds. It’s because the feature means how well users can move within a virtual space that adjusts to their position using motion controllers.
Companies use two types of head and position tracking simulators in VR headsets: Three Degrees of Freedom (3DoF) and Six Degrees of Freedom (6DoF). The latter is more popular among people because it allows them to look everywhere in the 360∘ space. However, 3DoF allows users to only move their head left, right, up, or down.
6. Virtual reality motion controllers
VR motion controllers are handheld devices that allow users to interact in a virtual environment. Using a motion controller, users can perform anything in a virtual environment such as — picking up things, or climbing a hill.
7. Batteries
Some of the virtual headsets that come with batteries that include rechargeable lithium batteries. Most of the time, these are single cell batteries with a nominal voltage of 3.85 volts.
How Does Virtual Reality Work?
So far, we’ve seen the components of a VR headset and what virtual reality is. Here, we will learn about how VR works in different forms.
1. Working of non-immersive VR
Non-immersive VR systems work with the assistance of components such as keyboards, mice, and controllers. For instance, think of how you’d use a computer system, or a video game. All the non-immersive virtual reality systems allow users to stay aware of their physical surroundings.
2. Working of semi-immersive VR
Semi-immersive virtual reality allows the users to partially interact with the virtual world. Users can move around the virtual world with a controller to decide their actions. Some of the examples of semi-immersive VR include: Flight simulators, Workbench and CAVE, and VRDD.
These systems are often present in the form of a 3D space or virtual environment. However, they may also include sensory inpurts such as audio vibration.
3. Working of fully immersive VR
Unlike the other two types of VR, fully-immersive VR systems completely immerse the user in the virtual world. These VR systems use advanced motion tracking techniques, high-quality 3D graphics, and other elements to create a real-life like experience.
In fully-immersive VR, various immersive technologies such as gestural controls, motion tracking, and computer vision create a sense of full immersion. Five immersive technologies that are used include:
- Panoramic 3D displays
- Surround sound acoustics
- Haptics and force feedback
- Smell replication
- Taste replication
These 5 technologies are used to create a sense similar to that of the real world.
How to Put On a VR Headset?
Each virtual reality headset comes with its own guide on activating the headset and putting it on. It’s because each VR headset is made differently and thus, a different guide for each headset.
So, here is a general guide on how to put on a VR headset:
- Put the headset down, right over your eyes.
- Slide and adjust the standard strap around your head so that the headset fits perfectly.
- Ensure that all the cables are well-adjusted.
Major challenges in VR Headsets
There are two major challenges that users face while using VR headsets: motion sickness and security risks. Here, we will discuss them in detail.
1. Motion Sickness
Motion sickness in VR is one of the major drawbacks one could note. It is some physical discomfort caused by prolonged use of the headset. The symptoms include drowsiness, headache, eye strain, fatigue, nausea, discomfort, and vomiting.
To avoid getting motion sickness, users should stay hydrated and take frequent breaks from the virtual environment. Additionally, high-end VR headsets have high frame rates which also help reduce motion sickness.
2. Security Risks
Most VR headsets come with eye tracking sensors as their standard feature. These eye tracking sensors can reveal a lot of information about the user, including their biometric data. Hence, creating a high risk for data breach. Additionally, malicious users can steal anyone’s virtual identity and misuse it.
The Bottom Line
Virtual reality is incredibly useful for various industries — education, entertainment, healthcare, and more. Additionally, the corporate sector may use VR systems to enhance productivity of the employees. However, the best case would be finding a middle ground and using such advanced technology only to an extent.







